More and more large-scale organizations are preferring cloud computing for their IT requirements mainly due to its unparalleled ability to bring together and share resources that are spread across the globe. By the year 2020, the global consolidated value of cloud computing services is expected to cross the $240 billion mark. The technology is immensely popular as it allows enterprises the convenience of doing away with unnecessary and excessive expenditure on:
Cloud Computing for Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Solutions

- Infrastructure
- Training & Knowledge Transfer
- New Software Accreditation
A constantly evolving technology, cloud computing has empowered small and medium businesses to access crucial business applications as well as upscale their infrastructural capabilities, all at a fraction of what it would cost them otherwise! This is essentially achieved by sharing enterprise computing and storage requirements on a global scale that reduces overhead costs.
Some of the prominent cloud computing merchants in the current market include:
- Amazon
- Microsoft
- Yahoo
Common cloud computing solutions on offer by most providers include:
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
- Storage-as-a-Service (StaaS)
Cloud computing strategies have taken business computing to the next level by capitalizing on the immense internet infrastructure that is available today. Some of the highlighted advantages enterprises can expect from a cloud solution include:
- Optimization
- Operational efficiency
- Collaborative Capabilities
- Fault Tolerant Solutions
- Reduced Costs
- Speed
It isn’t surprising therefore, that this technological innovation is finding its application in a variety of fields and domains, including disaster recovery. Numerous commercial enterprises of various sizes within the public and private sectors have a disaster recovery (DR) system in place to safeguard their data and operations. The main objective of these DR systems is to ensure business continuity and prevent organizations from suffering substantial damage in the form of losses to revenue, reputation, market share, growth prospects and much more.
Disaster Recovery through Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has been taking advantage of the various benefits of cloud computing solutions to mitigate the impact of natural and manmade disasters on business through destruction, loss of life and damage to the environment. Enterprise activities are always vulnerable to internal and external threats that can:
- interfere with operational procedures
- cause customer dissatisfaction
- impact revenue
- damage the organization’s brand name and reputation
Frequent system failures take their toll on resources, data and security. Organizations are continuously under pressure to downsize resource and asset requirements. Cloud computing techniques not only help in keeping company expenditure under control but also in increasing profits through efficient systems that are less prone to vulnerabilities.
Convenience is a key feature of cloud computing. Resources are made commonly available through the internet and are easily accessible. Provisioning and administration requirements are kept at a minimum. Besides, these systems are easy to maintain. Third party infrastructure is utilized, as and when required, for essential tasks such as core computing, software functionality and storage resource utilization.
Disaster recovery from an IT standpoint can be broadly classified into recovery solutions that are specific to data and applications. The organization’s DR strategy typically works towards engineering a backup database that takes over the host system when disaster strikes, thereby ensuring business continuity in operations.
A Disaster Management System (DMS) specific to Information and Communication Technology (ICT) principles must be able to address the four main stages in the DMS cycle – planning, response, recovery and post planning. The six principal aspects of any DMS system are:
- Web Portal
- Role Manager
- Workflow Engine
- Workflow Scheduler
- Workflow Monitor
- Notifcation
Vendors make disaster recovery solutions available for their customers as a backup service over the cloud.
Software as a Service (SaaS) – The customer uses the vendor’s applications that are made available through the cloud. A thin interface allows consumers to access applications through consumer units.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) – The customer creates, executes and maintains applications over the cloud. Programming languages and tools are made available by the vendor.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – The vendor provides the clients with computing resources to facilitate essential activities such as processing, storage and connectivity to build and operate software.
Cloud Storage as a Service (StaaS) – StaaS is a subset of IaaS that allows customers to store their data remotely in a manner that keeps it easily and instantly accessible. Effective cloud storage is crucial in order to address many key deliverables such as:
- Substantial availableness
- Trustworthiness
- Overall Performance
- Replication
- Data Regularity
Data Recovery in the Cloud
Technological advances and innovations along with robust systems and high speed connections have made it imperative for organizations to engineer operational models that can be quickly restored. Zero downtime is the business fraternity’s ultimate goal.
Data backups serve the important purpose of protecting company data from issues, human errors, hardware failures and impact from natural and manmade disasters. Disaster recovery essentially strategizes distributed computing and centralized storage. Its recovery objectives focus on three main categories – data, systems and applications.
The architectural framework of any cloud based storage system can be broadly categorized into four layers.
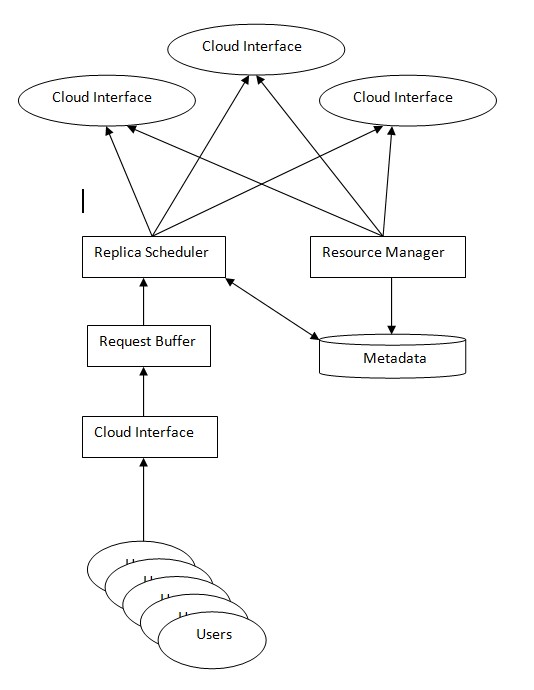
More often than not, emergency situations catch organizations completely unaware, leaving disaster management personnel very little time to adapt and act according to the situation. Restoring operations that are at the heart of an organization’s business framework as well as auxiliary functions is essentially what any foolproof disaster recovery strategy should aim at.
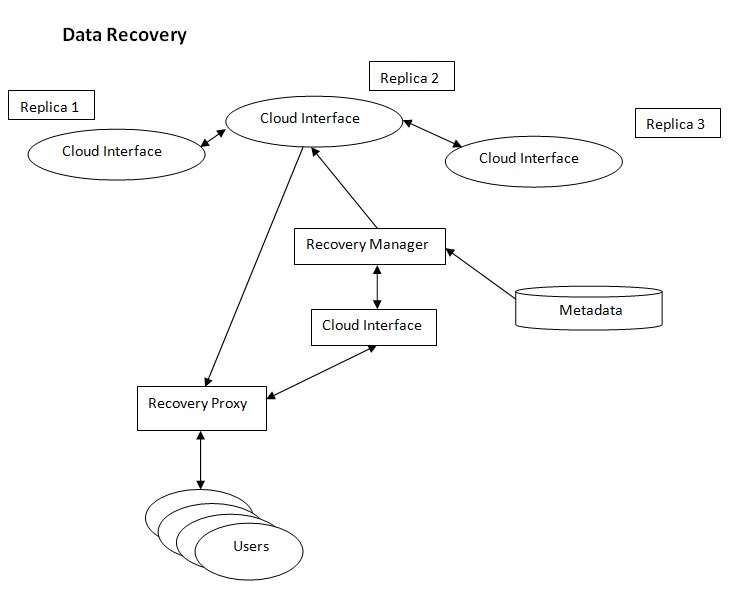
Disaster Recovery is primarily concerned with ensuring business continuity by reviving critical applications after operational disruptions in the event of a crisis. Carefully chalked out procedures and policies must be developed to restore an organization’s infrastructural capabilities as quickly as possible. A firmly established business continuity plan also instills confidence in investors, stakeholders and prospective customers alike.
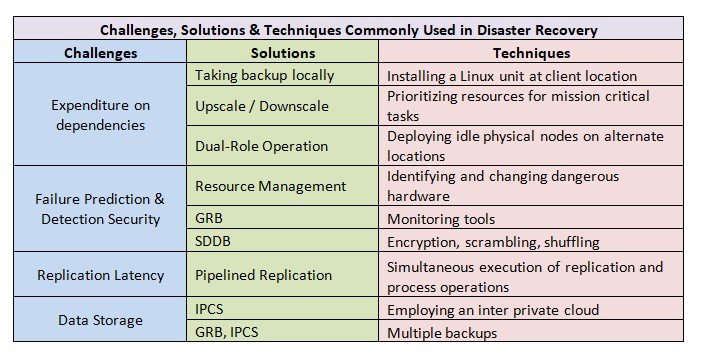
Issues, Concerns and Opportunities for Improvement
Adaptability is a major concern while using cloud computing techniques to install disaster recovery solutions. Collaboration between individuals, teams and departments while responding to an emergency, is a key factor.
The vast pools of data that are constantly generated from different quarters of a business are non-uniform in nature. Creating an effective DR strategy to backup non-uniform data on a large scale poses a major challenge. Transferring data to a safe location costs money and an enterprise must decide on a cost effective solution after carefully considering the criticality of the various types of information it generates that need to be protected.
Location also plays a key role as the data that is being backed up is legally bound by the laws of the geopolitical region where the storage devices are placed. Besides, trusting an outsider with sensitive business data is always a cause for unease and concern. Data protection and privacy related issues while adopting cloud computing technologies can be caused by a variety of issues including:
- Lack of sufficient certification
- Authorization/Audit Management
- Fault prone encryption algorithms
- Keys with inadequate protection
- Vendor risks
- Data Centers of dubious merit
- Inadequate disaster recovery strategies
Additionally, cloud computing solutions must be robust enough to ensure that outages across the entire infrastructural installation do not occur. Such failures can result in enormous financial losses even when they last for only a short duration of time.
More and more companies are migrating to the cloud to insulate their mission critical systems from being compromised. However, there is no generic free size that fits all and the ideal solution should be based on the specific needs of an organization’s operational challenges. Having said that, it can’t be denied that cloud computing based disaster recovery is a game changer that is taking organizational resiliency to a whole new level. The result being a satisfied clientele that translates into profits, brand equity and growth opportunities.

